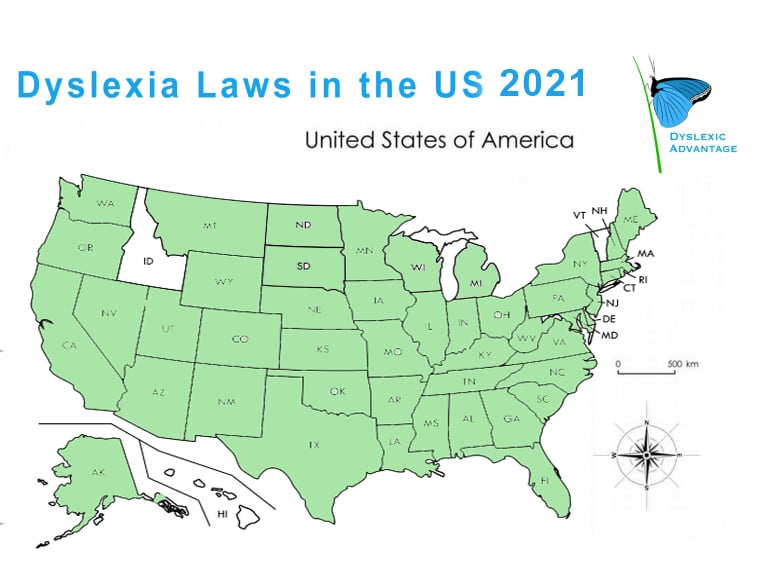
Here’s our 2021 snapshot of Passed Dyslexia Laws in the US. This is a rapidly changing time for dyslexia legislation, so please update us with corrections, changes, or newly passed laws. Huge thanks to the Dyslexic Advantage community, Decoding Dyslexia, and other leading dyslexia groups.
Just to clarify – dyslexia is formally recognized through out the US, but the overwhelming majority of states have also passed their own laws specifying requirements about dyslexia identification and teacher training. Unfortunately, there are still loopholes that seem to be developing and many requirements were postponed due to the COVID pandemic. There is a current practice of software companies trying to identify reading weaknesses and identifying those students as being at risk for dyslexia; the practice is not acceptable for identification. These students comprehensive issues are not identified, accommodations are not provided, qualification for free e-book and audiobook resources not provided, and specific remediation (including writing) not attended too. Get the facts if you have a student who you believe is dyslexic. Updated July 2021.
Only 3 states have no dyslexia-specific laws on the books. Some bills have been passed out of committee, but ultimately rejected.
NO Dyslexia-Specific Laws: Hawaii, Idaho, Vermont.
- Remember even if your state doesn’t have a specific Dyslexia law, federal law including the Department of Education formally recognizes Dyslexia for ALL states and has statement about dyslexia being mentioned specifically in IEPs and 504s.
It is important to mention dyslexia specifically by name as dyslexia is not simply a “reading disability”. Dyslexia has a long scientific, clinical, and educational history and the better a student’s educational needs are recognized, the more likely a student will have a well-suited educational program.
If you have any updates or corrections, please contact the team “at” dyslexicadvantage.org We would like to keep this list as current as possible. Addendum: Congratulations Alaska, Georgia, and Kansas for their new laws.
Alabama – 2015: Dyslexia added to Alabama Administrative Code
Alaska – 2018: H.B. 64 Establishment of dyslexia task force (task force only – no requirements for teacher training or student screening).
Arizona- 2019: SB 1318 Dyslexia screening and training. HB2362 K-3 Reading, specialist training. 2017: H.B. 2202 State dyslexia handbook. 2015: S.B. 1461 Definition of Dyslexia, Continuing Education for Teachers, Dyslexia Exemption for 3rd Grade Retention Law
Arkansas- 2013: Act 1294 Meeting the Needs of Children with Dyslexia in Public Schools
California- 2015: A.B. 1369 Identification and assessment, program for to improve educational programs for dyslexia prepared.
Colorado – 2008: H.B.1223 Training and identification.HB 19-1134 Identification and Interventions for Students with Dyslexia
Connecticut- 2016. 2015. 2014. An Act Concerning Dyslexia. Assessment and Teaching / Reading Tutor Training. Public Act 16-92. Public Act 15-97. Public Act 14-39.
Delaware- 2015: An Act to Amend Title 14 of the Delaware Code Relating to the Education of Students with Disabilities. Severe dyslexic students can waive state assessments. Evidence-based interventions.
Florida– 2017: HB 7069. Evidence-based and systematic, sequential, and multi sensory strategies added to Florida Educator Practices. Teacher renewals must include “explicit, systematic, and sequential approaches to reading instruction, developing phonemic awareness, and implementing multisensory intervention strategies. Teachers, reading coaches, school administrators taught to recognize dyslexia. 2015. John McKay Scholarships for IEP or 504 student to a ttend a public school other than assigned or private school for students with learning disabilities. State Board of Education Rule 6A-6.03018. Reading First.
Georgia – 2019: S.B. 48 required dyslexia screening and special training methods for those with dyslexia.
Hawaii- NONE: 2010 bill related to providing technical assistance to those with dyslexia was repealed.
Idaho– NONE
Illinois– 2018: H.B. 4639 Established dyslexia handbook. 2014: HB. 3700. Assessment, professional development, intervention.
Indiana- 2018: S.B. 217 Requires trained reading specialists to identify and modify teaching students with dyslexia. 2015: H.B. 1108. Defines dyslexia and requires professional training programs.
Iowa – 2018: S.F. 2360 Dyslexia task force established. 2016: ARC 2586c. Change in the Iowa Administrative Code to require teachers to know about dyslexia and the structure of language. 2014: Senate File 2319.
Kansas – 2018: H.B. 2602 Dyslexia task force* established. 2008: H.B. 5015. Screening, best practices for instruction, teacher prep – unfortunately this bill failed. *Task force only; no requirements for teacher training or student screening.
Kentucky– 2018: H.B. 187 Definition of dyslexia and screening toolkit. 2012: H.B. 69. Includes dyslexia, dysgraphia, dyscalcaulia, phonemic awareness.
Louisiana- 2013: (R.S. 17:7:11) identification, assessment, intervention, accommodations.
Maine – 2015: LD 231. Definition, screening, consultant.
Maryland – 2015: H.B. 278 Dyslexia Task Force. Task Force only. No requirements for teacher training or student screening.
Massachusetts -2018: General Law Chapter 7 Section 57A Screening procedures and protocols. Massachusetts General Law Chapter 15A Section 30. No resident of the commonwealth of MA with a developmental disability (including dyslexia or other SLD) should be required to take a standardized college entrance exam for a public-funded higher education institution.
Michigan – 2019: In 2016, Governor signed the 3rd Grade reading retention law. Section 388.1635a. Up to 5% funds for literacy screening. Mentions dyslexia screening option.
Minnesota – Revised Dyslexia Definition. K-12 Bill.The department must employ a dyslexia specialist. Dyslexia screening tool.
Mississippi– 2017: H.B. 1046 expansion of the previous bill, scholarship eligibility raised to Grade 12. 2012. H.B. 1031. Scholarship to provide dyslexic students with school choice.
Missouri– 2016: H.B. 2379 Sscreening for dyslexia in all public schools including charters.
Montana-: 2019: S.B. 140 (require sscreening and assistance for students with dyslexia) Montana Office of Public Instruction did add dyslexia to their special education guide.
Nebraska– Dyslexia Assistance Document Dyslexia Definition Revised.
Nevada– 2015: AB 341 and SB 391. Dyslexia screening and intervention.
New Hampshire– 2016: Passed HB 1644. AN ACT relative to screening and treatment for dyslexia and related disorders and establishing a reading specialist in the department of education.
New Jersey– 2014: PL2013 c 131, 105, 210. Dyslexia definition, minimum professional development, and screening for learning disabilities. Definition of dyslexia in administrative code. DOE Dyslexia handbook.
New Mexico– 2010: HB 2010. dyslexia definition, provide phonics-based tutoring as part of RTI.
New York- 2017: A08262. Guidance memorandum to all districts on dyslexia, dysgraphia, and dyscalculia.
North Carolina– 2017: S.B. 149 Dyslexia in the Education Code. Requires State Board to develop tools to ensure the identification of students with dyslexia and dyscalculia. Dyslexia Topic Brief.
North Dakota– NONE: 2019: H.B. 1461 pass and signed by governor 5/2019. Reading and dyslexia screening.
Ohio– 2011: Dyslexia training for k-4 teachers. Pilot project for intervention (year 3 finishes Oct 2015).
Oklahoma- 2017: H.B. 2008 Dyslexia Task Force H.B. 1128 2019 Dyslexia awareness and teacher training
Oregon – 2017: More dyslexia screening. Timeline changes to HB 2412. 2015. H.B. 2412. SB 612. Teacher training, dyslexia screening, dyslexia specialist.
Pennsylvania– 2014: A.B.69 Dyslexia screening and early literacy pilot program.
Rhode Island – 2016: H7052. Improve the performance of students with dyslexia in math, reading, and writing. 2012. H 7542. Definition and intervention.
South Carolina– 2013: South Carolina Task Force Report.
South Dakota– Unanimous approval H.B. 1175 H.B. 1133 awaiting Senate hearing (requires each school district to provide for students with learning disabilities).2020 Bill 1175 defining dyslexia introduced.
Tennessee– 2016: Say Dyslexia Law. Advisory committee, universal screening (through RTI or other), professional development. 2014. HB 1735 / SB 2002. Dyslexia is Real Bill.
Texas– 2018: Updated Dyslexia Handbook. 2009. 1995. Dyslexia Screening and Treatment, Licensed Therapists.
Utah– 2015: HB. 117 Pilot programs for professional development, literacy interventions K-5.
Vermont- In 2362.2.5, dyslexia is listed under special education. Eligibility for special education is specified. 2019. H406 Bill relating to screening for dyslexia introduced.
Virginia- 2016. HB 842. New teacher training in dyslexia.2017. SB1516. Dyslexia advisor in every school district.
Washington- 2009: RCW 28A.300.530 Individuals with Dyslexia – identification and Instruction. Handbook.
West Virginia– 2014: Definition of Dyslexia Dyscalculia.
Wisconsin– 2016: Education Guidance Document. 2014. Foundations of Reading Guide. Teacher Tests for new licenses. 2019 Assembly Bill 110. Guidebook related to dyslexia.
Wyoming– H.B. 297 2019. Reading Intervention and Guidance. Wyoming Individual Reading Plan. 2012: S.B. Assessment and intervention.R
Thanks Martha Youman and Nancy Mather for their Update on Dyslexia Laws 2018.
2018 Youman MatherDownload pdf HERE.
The paper is also available on Research Gate here.
Other Resources: Decoding Dyslexia MD Dyslegia Decoding-Dyslexia-State-Laws















I’m a senior in high school who is dyslexic and dysgraphic though my diagnosis did not come for many years. I attended elementary school at one of Pennsylvania’s top schools, and I was told I was a strong reader and that my writing was age appropriate. When we were relocating, I had to take a cognitive test for a new school, and that is when my parents learned about the significant disparity among the scores on the test. It was another two years, three states, multiple assessments, and thousands of dollars before my parents finally heard the words dyslexia and dysgraphia–and this is despite telling evaluators that dyslexia runs in my family. As a result of the delays, I missed the crucial systematic reading instruction I needed when I was an emerging reader, and my brain was better able to form the neuro-literacy connections. Instead, I spent the four years with rotating tutors and therapists after school and during the summers. That was also thousands of dollars, not to mention the emotional toll of not getting to play sports and feeling stupid and unworthy.
Many children with stealth dyslexia are never diagnosed; if they are, it’s when they are older students. Either way, most do not get the help they need.
When I look back, I realize there were two critical decisions that contributed to the unnecessary delays in treatment. The first was when my reading skills were observed, and false assumptions were made. Neither my teachers nor the school’s reading specialist tested decoding with nonsense words. It’s so simple and yet….? The second problem was that neither Pennsylvania (Philadelphia suburb) nor New York City education psychologists say the word dysgraphia or dyslexia–at least, at that time, they didn’t. The decision puts parents at a huge disadvantage for advocating for their children. I can’t imagine a good reason for such a harmful policy.
When I read the laws in the various states on this website, I appreciate that there is progress and many states are now aware of some of the issues, but the laws in most states are simply too little and too late. Only Florida makes it mandatory that teachers are trained to instruct all students using the proven systematic reading instruction that benefits all students and is what dyslexic students need. Economically, logically, and humanely it is the best way to ensure ALL children have the tools they need to succeed. Any other policy risks too many children not being identified, and if they are, it is too late, and there is simply no way at that point for most children to get the costly amount of help they need.
I also recently read that several states have announced they are committing all or a portion of their unused Covid relief education funds for structured reading programs to support dyslexia. I hope this is true and that more states will consider this. However, it is important to take note that nothing short of teaching everyone using the same method will amount to the necessary level of payoff. Support for programs that support better assessments is misplaced. Providing structured reading for all means there is no need for assessment, costly remediation, and unfathomable social and emotional harm to children. Follow Florida’s lead America!
Hi AJ,
It is a tragedy the current status of dyslexia identification. Even with the dyslexia laws – they are already getting chipped away at in many ways – 1 minute screeners misidentify and also under-identify.
Teacher training is getting better, but there is such a long way to go and too few supports for middle and high school students. Yes it is true that some COVID relief funds are going to high impact tutors – but these do not necessarily mean tutors who have had any dyslexia training – so it may not be as impactful as it could have been.
Still – it’s a start.
Great for your parents and great for you. Dysgraphia is woefully unidentified and yet it hold so many people back in higher education. Knowledge is power – and it’s great tosee the next generation being more outspoken and also recognizing dyslexic strengths.
Fernette
Hi guys! Iowa laws are not up to date. There is a new task force law that passed this year! Here is information on that. http://www.decodingdyslexiaiowa.org/2018-legislation/. Thanks!
Thanks for sharing and Congrats!!! Its amazing seeing somecmuch progres!
Kansas just passed HB 2602 – Creating a Dyslexia Task Force!!!
Wow – thanks for the updates, Jennifer! You folks are working so hard and getting results! It’s wonderful to also begin seeing laws regarding dyscalculia and dysgraphia. If it’s not specified, it’s definitely missed. Thank you for helping keep us updated and congrats Decoding Dyslexia – all 50 states!
NC passed HB 149. Most important part is the definition of dyslexia in the Education Code. Requires review of screening and teacher continuing education but not very specific on these. Full bill here: http://www.ncleg.net/Sess…/2017/Bills/House/PDF/H149v4.pd
The Massachusetts law is not helpful at all on the level of reading instruction or teacher training or any helpful practical way for supporting kids to learn to read.
Pending Legislation would screen all kids for deficits in the key indicators, phonemic awareness, naming speed and letters and knowledge. This map is not really usefully showing the reality of kids being denied FAPE when they have dyslexia. In Massachusetts, we wait for kids to fail, find them late, refuse to say dyslexia so rarely provide evidenced-based instruction for dyslexia and then waive a test score? That’s a pathetic answer to a serious issue?
Thanks for this clarification, Nancy. We hope the pending legislation passes!
Agreed… the current Massachusetts law is not helping my third grader succeed.. I’ve been fighting for better services since January of grade 1 and keep getting the minimum. Very discouraging experience as a mother and as an educator!!!!
VA also has SB1516 that also went into effect July 1 2017, requiring a dyslexia advisor at each district level. Here is the legislative history. https://lis.virginia.gov/cgi-bin/legp604.exe?171+sum+SB1516
Thank you for this great resource
Kristin Kane
Thanks Kristin, I’ll add it to our list! Fernette
Maryland only passed a task force – whose recommendations have not been acted on. There are currently no requirements related to the education of dyslexic students.
Thanks for posting this!
Oregon passed two additional bills in 2017 that amend the 2015 bills.
— SB 1003 (2017) provides more clarification (next steps) to SB 612 and adds a screening component for risk factors of dyslexia.
— SB 221 (2017) provides some timeline changes to HB 2412 as well.
Thanks, Diana! I’ll add!
How could I help to have these laws in NJ
I meant *these. I would like to help.
Thanks, Cynthia! To get involved at your state level, we usually recommend that people get in touch with their local Decoding Dyslexia Chapter. For your state, that would be Decoding Dyslexia New Jersey. If you’re on Facebook, we’ll also announce big events for the Dyslexia community on our Facebook feed Dyslexic Advantage on Facebook. Thanks for joining the fight!